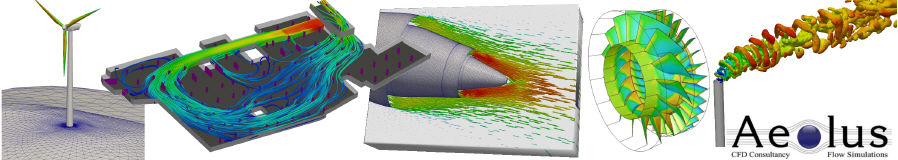
Computational Fluid Dynamics
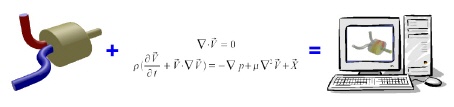
CFD is a letterword for Computational Fluid Dynamics. The term 'CFD' is used for a specific technology that models gas and liquid flows on computers. It's final goal depends on the situation, but more often than not it is one of the following:
- Insight: to provide a complete insight in flows of gasses and/or liquids to be able to answer specific engineering questions.
- Virtual Prototyping: to test virtually with a computermodel a possible improvement of a device, before going along the route of prototyping and physical testing.
- Speed of development: to develp new designs faster and to make them ready for market faster.
- "What if"-questions: Using modeling, you can answer what-if questions that would have remained unanswered otherwise.
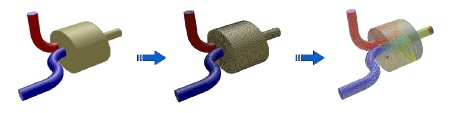
CFD Process
- Preprocessing: the geometry of the flow domain is brought into the computer and a computational mesh is designed/constructed
- Solving: the flow with its physical phenomena is being calculated.
- Postprocessing: the results of the simulation are being processed into clear pictures, contourplots, numerical values, .... These results are analysed with the critical eyes of an engineer.
Numerical Outputs from simulations
- Velocity vectors
- Stream lines
- Pathlines
- Contour plots on arbitrary cut planes of any flow variable (velocity components, temperature, turbulence, shear stresses, vorticity, ...)
- Animated solution to render the time dependancy of the solution